Audio Self-supervised Learning: A Survey (2) Audio
논문 : Audio Self-supervised Learning: A Survey
연관 포스트: Audio Self-supervised Learning: A Survey (1) A General Overview
분류 방식은 논문에는 Contrastive Model 중에서 Auto-Encoding/Siamese/Clusetering 그리고 Contrastive Model로만 분류가 되어 있습니다.
세부적인 분류는 “Audio Self-supervised Learning: A Survey” 설명만 읽고 임의로 분류했기에 분류가 틀릴 수도 있습니다.
1. Predictive Models
1) Auto-Encoder
a) Basic Encoders
- Audio2Vec & Speech2Vec
- Word2Vec: CBow & Skip-gram에서 영감받음
- CBoW는 이전과 이후의 frame들을 가지고 가운데 비어있는 spectrogram frame 복원
- CBoW는 acoustic scene classification에서 좋은 결과
- Skip-gram은 주어진 frame으로 이전과 이후 frame 예측
-
Audio2Vec Speech2Vec explicit한 도움 필요 없음
(supervision한 부분 완전 제거)각 단어에 맞는 audio slice segmentation을 위한
explicit forced alignment technique 사용CNN 기반 RNN 기반 MFCC Mel-spectrogram TemporalGap
(같은 audio clip 내에 random하게
sampled된 data 사이의 시간 차이 예측)- - TemporalGap이 CBoW나 Skip-gram보다 더 좋은 결과를 내진 않았지만, pretext task를 상대적인 시간 측정이라는 새로운 관점 제시
- Carr et al.
- audio patch suffle » 다시 순서를 맞추는 방법 (permutation & jigsaw puzzle)
- “Shuffle and Learn” 논문에서 아이디어 얻음 (audio classification 관련 논문)
- end-to-end 학습을 위해 재정렬하는 방식을 개선: differential ranking(어떤 건지 확인 더 필요)
-
PASE & PASE+ (The Problem Agnostic Speech Encoder)
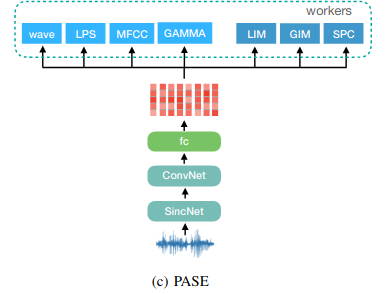
- CNN encoder 1개 + 여러개의 neural decoder(worker)
- encoding된 값을 decoder에서 regression 혹은 binary discrimination
- regression: recovering raw waveform, log power spectrogram, MFCCs, prosody(운율)
- binary discrimination: contrastive learning: maximizing local and global mutual information(LIM/DIM과 유사), sequence predictive coding optimize(VQ-VAE와 유사)
- unique expression of speaker voiceprint, phonemes, emotion
- raw waveform » SincNet » encoder input
- PASE+
- data augmentation
- more efficient workers
- Quasi-RNN(QRNN): long-term dependencies capture에 더 효과적
b) Auto-regressive Predictive Coding (APC)
c) Masked Predictive Coding (MPC)
- Masked Acoustic Model (MAM)
- audio input의 일부분을 masking한 후, 전체 input reconsturct
- reconstruction error 최소화
- Mockingjay

- Mel-Spectrogram
- random making input을 transformer를 사용하여 coding
- projection(2 layer MLP + layer normalization)한 후에 frame 예측에 사용
- transformer와 projection layer은 동시에 L1 reconstruction loss 최소화
- transformer의 self-attention의 효과에 대한 연구와 visualization tool 제작
- Audio ALBERT
- Mockingjay와 똑같은 구조
- transformer encoder layer parameter 값 동유
- 빠른 추리(inference), 빠른 학습 속도
- performance 유지: speaker classificaion과 phoneme(음소: ㄱ,ㄴ,ㄷ,ㅏ,ㅓ,ㅗ …) classificaion
- TERA (Transformer Encoder Representations from Alteration)
- continuous » randomness segments
- channel 측 방향으로 masking (특정 frequency all zero)
- Gaussian noise 추가
- 2.Mockingjay와 3.Audio ALBERT보다 좋은 결과
- performance 향상: speaker classificaion, phoneme classificaion, keyword spotting
- ASR task에서 기대해 볼 만한 성능: Librispeech, TIMIT dataset
d) Non-Auto-regressive Predictive Coding (NPC)
- DAPC
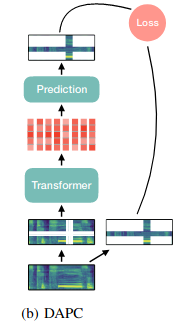
- time뿐만 아니라 frequency도 함께 masking
- 전체가 아닌 mask 부분만 reconstruction » L1 reconstruction error 최소화
- CBoW의 확장
- SpecAugment로 쉽게 만들 수 있음
2) Siamese
a) BYOL
- BYOL-A
- 하나의 audio로 negative한 sample 없이 학습
- log mel-filterbank
2. Contrastive Models
a) SimCLR approch
- LIM Model
- raw waveform 사용
- 같은 utterance에서 나온 chunk들의 encoded representation 최대화
- COLA & Fonseca et al.
- time-frequency(spectrogram 형태) feature에서 시간(temporal) 축으로 positive sampling
- patch에 data augmentation
- random size cropping
- Gaussian noise addition
- mix-back (incoming patch + background patch)
- CLAR
- raw waveform이랑 time-frequency feature에 data augmentation
- 다양한 augmentation에 대한 연구 진행
- 상당히 적은 수의 labelled data를 사용하여 contrastive loss를 결합하면 SSL만 사용했을 때보다 수렴 속도, representation effectiveness의 개선이 있었음
- CLAR 정리
- Wang
- raw waveform과 spectral representation 사이의 호응(agreement) 최대화
- Audioset, ESC-50 downstream task에 효과적
3. Contrastive Predictive Coding (CPC)
-
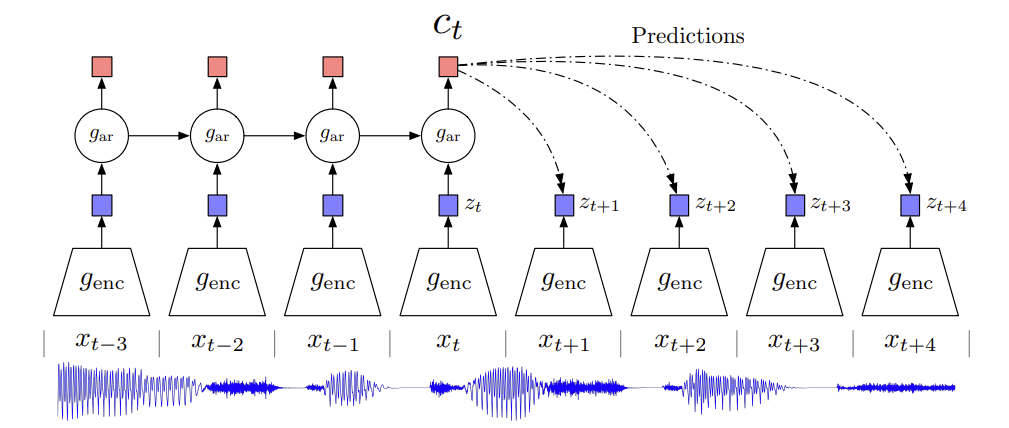
- CPC: auto-regresive model의 latent space를 사용해서 미래 값 예측
- Audio는
- strided convolution을 사용하여 raw waveform encoding
- GRU가 과거의 timesteps을 통합하여 context vector 만듦
- contrastive loss(infoNCE)
- context vector $c_t$를 주고, noise representations과 참값 비교
- $z_n^-$: $z_{t+\tau}$ 분포에서 sample된 negative data point, sequence $z$에서 random sampling \(L(c_t, z_{t+\tau},z^-_{n\in [1,N-1]}) = \mathbb{E}[-log\frac{exp(c^T_tz_{t+\tau})}{exp(c_t^Tz_{t+\tau})+\sum_{n=1}^{N-1}{exp(c_t^Tz_n^-)}}\)
- WavAugment library
- pitch modification
- add noise
- reverberation
- band regect filtering
- time masking …
- CPC ver2.
- 1 layer GRU » 2 layers LSTM
- linear prediction » multi-head transformer
-
“Wav2Vec”s
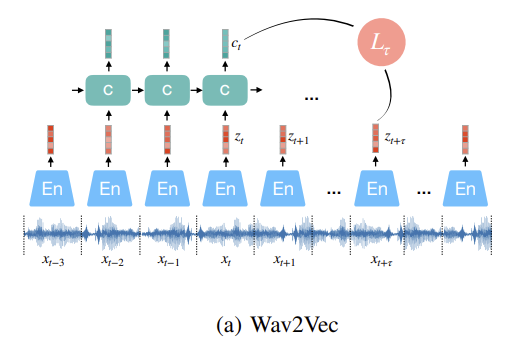
- (a) Wav2Vec
- 위 CPC와 다르게 fully convolutional
- 아래 cnn: audio representation 만듦
- 위의 cnn: 각 timestep의 context vector에 대한 global context information capture
- phoneme-based ASR » character-bases ASR
-
contrastive loss for wach step $k=1, \cdots, K:$
\[L_k = -\sum_{i=1}^{T-k}(log \ \sigma (z^T_{i+k}\ h_k(c_i)) + \lambda_{\tilde{z} \sim p_n} \mathbb{E}[log\ \sigma (-\tilde{z}^T\ h_k(c_i))]) \\ L = \sum_{k=1}^KL_k\]- sigmoid $\sigma(x)={1}\ / \ (1+exp(-x))$
- $\sigma (z^T_{i+k}\ h_k(c_i))$: $\ z_{i+k}$가 true sample일 확률
- $h_k(c_i)=W_kc_i+b_k$: step-specific affine transformation
- expectation $\mathbb{E}$ 는 $p_n(z)=\frac{1}{T}$ 에서 10개의 negative sample을 뽑고 $\lambda$는 negative의 개수 (T: sequence length)
- 학습 후에는 log-mel filterbank 대신에 $c_i$를 input으로 넣어줌
- 위 CPC와 다르게 fully convolutional
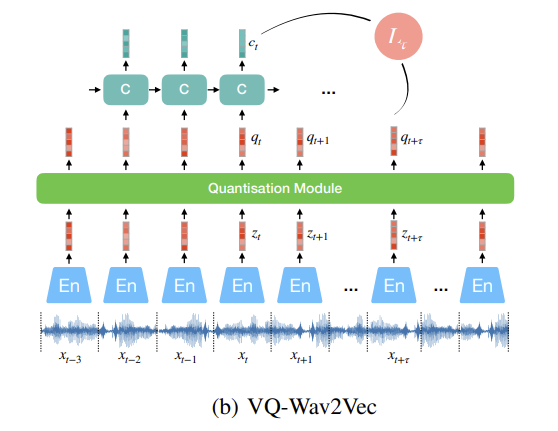
- (b) VQ-Wav2Vec
- audio representation 이산화하기 위해 wav2vec encoder 다음에 quantisation moodule 추가
- 고정된 크기의 codebook $e \in \mathbb{R}^{V \times d}$ 에 있는 것과 가장 유사한 representation 찾기 (V representation with of size d)
- argmax은 back-propagation 안 됨
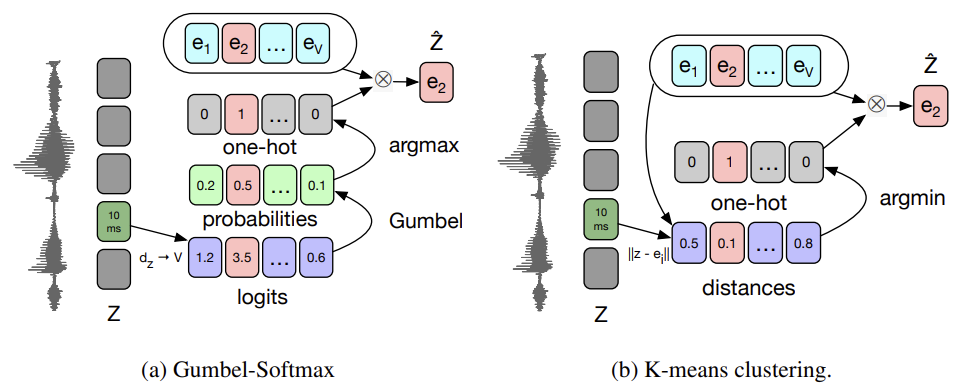
- Gumbel-Softmax나 online k-means clustering 사용
- VQ-VAE나 vector-quantized autoregressive predictive coding과 유사
- codebook 1개만 사용하면 실제로 사용되는 codeword가 적어서 mode collapse 발생 » product quantization처럼 multiple codebooks 사용
- product quantization은 여러개의 codebook에서 quantized된 representation을 고르고 concat하는 것과 동일 product quantization 설명된 blog
- 각 codebook에서 entry 하나씩 » concat » linear transformation
- group g의 v-th codebook을 고를 확률
\(p_{g,v}=\frac{exp((l_{g,v}+n_v)/\tau)}{\sum_{k=1}^{V}exp((l_{g,k}+n_k)/\tau)}\)
- $l\in \mathbb{R}^{G \times V}$: encoded dense representation » projection’s logits (V entries로 이루어져 있는 G개의 codebooks)
- $n=-log(-log(u)) \qquad u \sim U(0,1): uniform$
- $\tau$: non-negative temperature parameter
- codeword i in group g는 $argmax_i \ p_{g,i}$
- K-means clustering은 dense representation z와 가까운 codeword 선택하기
- wav2vec loss에 term 추가
\(L=\sum_kL_k+(\Vert stopgrad(z) - q\Vert^2 + \gamma\Vert z - stopgrad(q)\Vert^2)\)
codeword q가 encoder output과 비슷해지고, 각 encoder의 output이 codeword와 가까워지게(K-means clustering의 one centroid)
- wav2vec loss에 term 추가
\(L=\sum_kL_k+(\Vert stopgrad(z) - q\Vert^2 + \gamma\Vert z - stopgrad(q)\Vert^2)\)
- 그 후에 BERT model에 넣어서 학습
- audio representation 이산화하기 위해 wav2vec encoder 다음에 quantisation moodule 추가
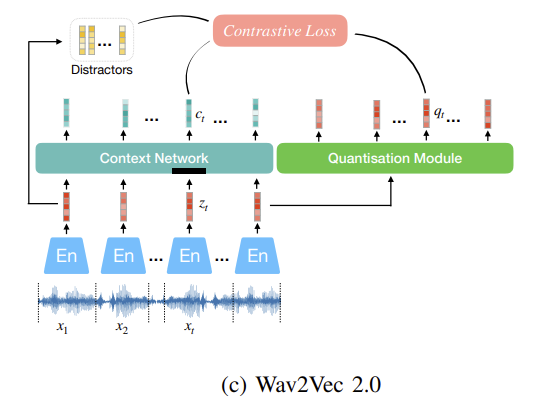
- (c) Wav2Vec 2.0
- MPC
- 이전 wav2vec 모델은 forward만 가능 » bidirectional MPC
- InfoNCE contrast loss 사용
- raw waveform multiple 1D-CNN으로 encoding
- mask 후 transformer
- contextual representation이 주어졌을 때, 정답값과 distrator와의 contrast
- quantized vector는 loss 계산에만 사용
\(L=\mathbb{E}[-log\ \frac{exp(c_t^Tq_t/\tau)}{\sum_{\tilde{q}\sim Q_t} exp(c_t^T \tilde{q}/\tau)}]\)
$\tilde{q}\sim Q_t$: $q_t$와 K개의 distracter 포함 - regularization은 diversity loss $L_d$로, model이 V codebook을 비슷하게 사용하도록 \(L_d = \frac{1}{GV}\sum_{g=1}^G -H(\bar{p}_g) = \frac{1}{GV}\sum_{g=1}^G \sum_{v=1}^V\bar{p}_{g,v}\ log\ \bar{p}_{g,v}\)
- 현재 SOTA
- speech recognition task를 위해서는 pre-training과 testing 조건을 잘 맞춰야함
- 다양한 domain의 data 학습하는 것이 generalization에 도움됨
- (a) Wav2Vec
댓글남기기